Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (26): 4208-4214.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0933
Previous Articles Next Articles
Irradiation with erbium, chromium:yttrium scandium gallium garnet laser alters shear bond strength to primary tooth dentin
Liang Yun1, Shi Jian-jie2, Chen Ke3, Luo Zhen-shan1, Deng Wen-xin1
- 1Liwan Hospital, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510175, Guangdong Province, China; 2the Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510150, Guangdong Province, China; 3Guangzhou Women and Children’s Medical Center, Guangzhou 510623, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2018-02-09 -
Contact:Shi Jian-jie, Chief physician, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510150, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Liang Yun, Master, Physician, Liwan Hospital, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510175, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. S2013010014879; the Science and Technology Research Plan of Guangzhou, No. 201510010160
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liang Yun, Shi Jian-jie, Chen Ke, Luo Zhen-shan, Deng Wen-xin. Irradiation with erbium, chromium:yttrium scandium gallium garnet laser alters shear bond strength to primary tooth dentin[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(26): 4208-4214.
share this article
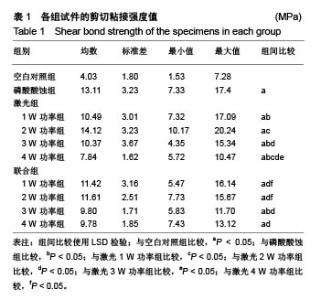
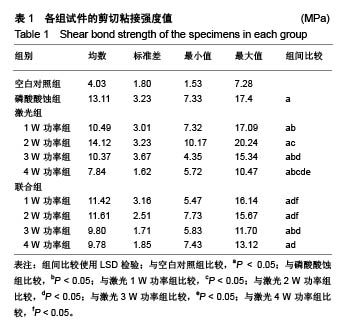
2.1 试件剪切粘接强度测试结果 表1显示了牙本质各小组样本的剪切粘接强度均值、标准差、最小值及最大值。各小组试件剪切粘接强度经Levenece方差齐性检验,按α=0.10水准,可认为10组资料总体方差齐性(F=1.556,P=0.105 > 0.10)。数据满足方差齐性要求,对10组剪切粘接强度数据进行完全随机设计的方差分析发现有差异统计学意义(F=4.625,P=0),可认为不同方法预处理后乳牙本质与树脂间剪切粘接强度不同,还需进一步作多重比较。经多个样本均数间两两比较的LSD检验发现:空白对照组剪切粘接强度值低于其余9组(P <0.05);磷酸酸蚀组剪切粘接强度值高于激光1,3,4 W功率组及联合3 W功率组(P < 0.05);激光1 W功率组剪切粘接强度值低于激光2 W功率组(P < 0.05),高于激光4 W功率组(P < 0.05);激光2 W功率组剪切粘接强度值高于激光3 ,4 W功率组及联合1,2,3,4 W功率组(P < 0.05);激光3 W功率组剪切粘接强度值高于激光4 W功率组(P < 0.05);激光4 W功率组剪切粘接强度值低于联合1,2 W功率组(P < 0.05);联合组内,不同功率组间两两比较差异均无显著性意义。"
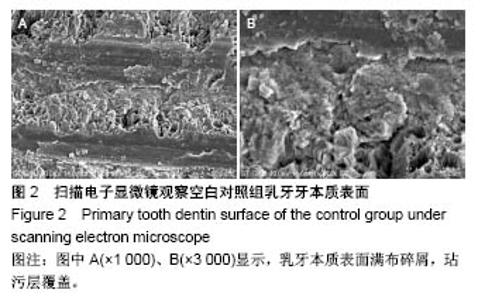
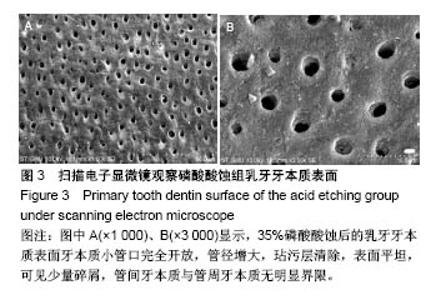
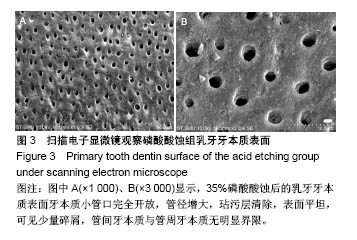
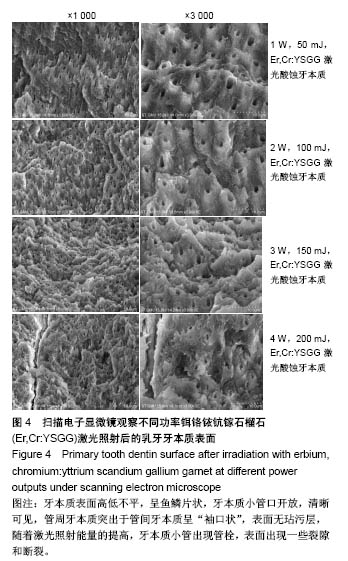
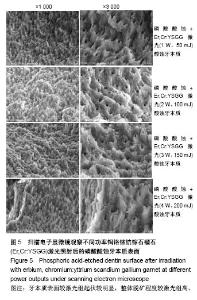
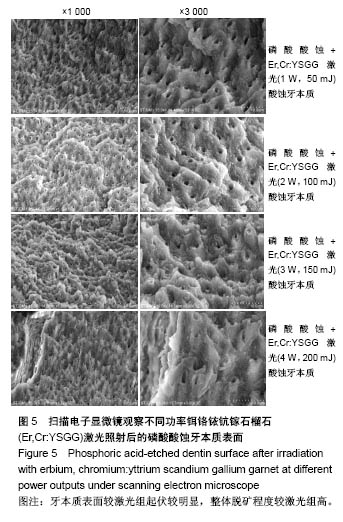
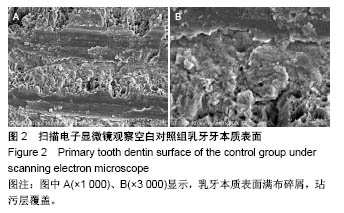
2.2 扫描电子显微镜观察结果 空白对照组乳牙本质表面满布碎屑,玷污层覆盖(图2)。 磷酸酸蚀组乳牙牙本质表面牙本质小管口完全开放,管径增大,玷污层清除,表面平坦,可见少量碎屑,管间牙本质与管周牙本质无明显界限(图3)。 激光组牙本质呈现干净、粗糙不规则的表面,扫描电子显微镜下牙本质表面高低不平,呈鱼鳞片状,牙本质小管口开放,清晰可见,管周牙本质突出于管间牙本质呈“袖口状”,表面无玷污层,无炭化及热损伤迹象,随着激光照射能量的提高,牙本质小管出现管栓,表面出现一些裂隙和断裂(图4) 激光1 W功率组、联合1 W功率组牙本质表面较其他组平坦,起伏没那么明显,管周牙本质突出不明显;激光2 W功率组牙本质表现为高低不平的蜂窝状和烟囱样羽状外观,不规则的鳞片状结构增多,牙本质小管开放但未扩大,管周牙本质较管间牙本质突出最明显;激光3 W功率组牙本质表面粗糙化和不规则程度提高,牙本质小管管径减小或部分封闭,管间牙本质去除较激光1,2 W功率组显著;激光4 W功率组可见牙本质裂缝和断裂的出现,表面消融的较明显,色泽变白。 联合组牙本质表面较激光组起伏更明显,整体的脱矿程度比激光组更高,联合3 W功率组比激光3 W功率组牙本质小管内栓塞、闭合现象更显著(图5)。"
| [1] Soares CJ,Fonseca RB,Martins LR,et al.Esthetic rehabilitation of anterior teeth affected by enamel hypoplasia: a case report.J Esthet Restor Dent.2002;14(6):340-348.[2] Buonocore MG.A simple method of increasing the adhesion of acrylic filling materials to enamel surfaces.J Dent Res. 1955; 34(6):849-853.[3] Pires PT,Ferreira JC,Oliveira SA,et al.Shear bond strength and SEM morphology evaluation of different dental adhesives to enamel prepared with ER:YAG laser.Contemp Clin Dent. 2013; 4(1):20-26.[4] Beer F,Buchmair A,Korpert W,et al.Morphology of resin-dentin interfaces after Er,Cr:YSGG laser and acid etching preparation and application of different bonding systems. Lasers Med Sci. 2012;27(4):835-841.[5] Hossain M,Nakamura Y,Yamada Y,et al.Effects of Er,Cr:YSGG laser irradiation in human enamel and dentin: ablation and morphological studies.J Clin Laser Med Surg. 1999;17(4): 155-159.[6] Santini A,Plasschaert AJ,Mitchell S.Effect of composite resin placement techniques on the microleakage of two self-etching dentin-bonding agents.Am J Dent.2001;14(3):132-136.[7] Yap AU,Pearson GJ,Billington RW,et al.An in vitro microleakage study of three restorative techniques for Class II restorations in posterior teeth.Biomaterials. 1996;17(21): 2031-2035.[8] Wigdore H,Abt E,Ashrafi S,et al.The effect of lasers on dental hard tissues.J Am Dent Assoc. 1993;124(2):65-70.[9] Margolis F.The Star Wars of dentistry.Using the erbium laser to treat tooth decay.CDS Rev. 2002;19:26-29.[10] Rizoiu I,Kohanghadosh F,Kimmel AI,et al.Pulpal thermal responses to an erbium,chromium ysgg pulsed laser hydrokinetic system.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1998;86(2):220-223.[11] Eversole LR,Rizoiu I,Kimmel AI.Pulpal response to cavity preparation by an erbium, chromium:YSGG laser-powered hydrokinetic system.J Am Dent Assoc. 1997;128(8):1099-1106.[12] Hossain M,Nakamura Y,Yamada Y,et al.Compositional and structural changes of human dentin following caries removal by Er,Cr:YSGG laser irradiation in primary teeth.J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2002;26(4):377-382.[13] Lin S,Pan D,Lin Q,et al.Evaluation of phase, microstructure and composition of human dentine after Er,Cr:YSGG laser irradiation.J Nanosci Nanotechnol.2011;11(3):2421-2426.[14] Hossain M,Kimura Y,Nakamura Y,et al.A study on acquired acid resistance of enamel and dentin irradiated by Er,Cr:YSGG laser.J Clin Laser Med Surg.2001;19(3):159-163.[15] Al-Omari WM,Palamara JE.The effect of Nd:YAG and Er,Cr:YSGG lasers on the microhardness of human dentin. Lasers Med Sci.2013;28(1):151-156.[16] Vergauwen TE,Michiels R,Torbeyns D,et al.Investigation of Coronal Leakage of Root Fillings after Smear Layer Removal with EDTA or Er,Cr:YSGG Laser through Capillary Flow Porometry. Int J Dent.2014;2014:593160.[17] Wolfram H,Volker R,Elke A,et al.Principles and phenomena of bioengineering with glass-ceramics for dental restoration.J Eur Ceram Soc.2007;27(2-3):1521-1526.[18] Bouillaguet S,Ciucchi B,Jacoby T,et al.Bonding characteristics to dentin walls of class II cavities, in vitro.Dent Mater. 2001; 17(4):316-321.[19] Luthy H,Marinell CP,Scharer P.Factors influencing metal-resin tensile bond strength to filled composites.Dent Mater.1990;6(2): 73-77.[20] Masoumeh M,Leila E,Fekrazad R,et al.The effect of Er,CrYSGG laser and air abrasion on shear bond strength of a fissure sealant to enamel.J Am Dent Assoc. 2010;141(2):157-161.[21] Bona D.Shear vs tensile bond strength of resin composite bonded to creamic.Dent Res. 1999;74:1591-1596.[22] Wang X, Zhang C, Matumoto K. In vivo study of the healing processes that occur in the jaws of rabbits following perforation by an Er,Cr:YSGG laser.Laser Med Sci. 2005;20(1):21-27.[23] Yamada MK,Uo M,Ohkawa S,et al.Three-dimensional topographic scanning electron microscope and Raman spectroscopic analyses of the irradiation effect on teeth by Nd:YAG, Er: YAG, and CO(2) lasers.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2004;71(1):7-15.[24] Cardoso MV,De Munck J,Coutinho E,et al.Influence of Er,Cr:YSGG laser treatment on microtensile bond strength of adhesives to enamel.Oper Dent.2008;33(4):448-455.[25] Ramos TM,Ramos-Oliveira TM,Moretto SG,et al.Microtensile bond strength analysis of adhesive systems to Er:YAG and Er,Cr:YSGG laser-treated dentin.Lasers Med Sci. 2014;29(2): 565-573.[26] Ayar MK,Yildirim T,Yesilyurt C.Effects of Er,Cr:YSGG laser parameters on dentin bond strength and interface morphology.Microsc Res Tech.2015;78(12):1104-1111.[27] Sungurtekin E,Oztas N.The effect of erbium, chromium: yttrium-scandium-gallium-garnet laser etching on marginal integrity of a resin-based fissure sealant in primary teeth. Lasers Med Sci. 2010;25(6):841-847.[28] Cvikl B,Moser G,Wernisch J,et al.The impact of Er,Cr:YSGG laser on the shear strength of the bond between dentin and ceramic is dependent on the adhesive material.Lasers Med Sci. 2012;27(4):717-722.[29] Issar R,Mazumdar D,Ranjan S,et al.Comparative Evaluation of the Etching Pattern of Er,Cr:YSGG & Acid Etching on Extracted Human Teeth-An ESEM Analysis.J Clin Diagn Res. 2016;10(5): ZC01-05.[30] Malkoc MA,Tasdemir ST,Ozturk AN,et al.Effects of laser and acid etching and air abrasion on mineral content of dentin. Lasers Med Sci.2011;26(1):21-27.[31] Yildirim T,Ayar MK,Yesilyurt C.Influence of different Er,Cr:YSGG laser parameters on long-term dentin bond strength of self-etch adhesive.Lasers Med Sci. 2015;30(9): 2363-2368.[32] Verma M,Kumari P,Gupta R,et al.Comparative evaluation of surface topography of tooth prepared using erbium, chromium: Yttrium, scandium, gallium, garnet laser and bur and its clinical implications.J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2015;15(1):23-28.[33] Lee BS,Lin PY,Chen MH,et al.Tensile bond strength of Er,Cr:YSGG laser-irradiated human dentin and analysis of dentin-resin interface.Dent Mater.2007;23(5):570-578.[34] Garbui BU,de Azevedo CS,Zezell DM,et al.Er,Cr:YSGG laser dentine conditioning improves adhesion of a glass ionomer cement.Photomed Laser Surg.2013;31(9):453-460.[35] Kinoshita J,Kimura Y,Matsumoto K.Comparative study of carious dentin removal by Er,Cr:YSGG laser and Carisolv.J Clin Laser Med Surg.2003;21(5):307-315.[36] Shahabi S,Zendedel S.Atomic analysis and hardness measurement of the cavity prepared by laser.Lasers Med Sci. 2010;25(3):379-383.[37] Oznurhan F,Olmez A.Morphological analysis of the resin-dentin interface in cavities prepared with Er,Cr:YSGG laser or bur in primary teeth.Photomed Laser Surg. 2013;31(8):386-391.[38] Hossain M,Nakamura Y,Yamada Y,et al.Microleakage of composite resin restoration in cavities prepared by Er,Cr:YSGG laser irradiation and etched bur cavities in primary teeth.J Clin Pediatr Dent.2002;26(3):263-268.[39] Shafiei F,Memarpour M,Fekrazad R.Sealing of silorane-based composite in laser-prepared primary teetheffect of acid etching. Pediatr Dent.2014;36(5):378-383.[40] Malekafzali B,Fekrazad R,Mirfasihi A,et al.Comparison of microtensile bond strength of a resin composite to enamel conditioned by acid etching and Er,Cr:YSGG laser in human primary teeth.Eur Arch Paediatr Dent.2015;16(1):57-62.[41] De Menezes Oliveira MA,Torres CP,Gomes-Silva JM,et al.Microstructure and mineral composition of dental enamel of permanent and deciduous teeth.Microsc Res Tech. 2010;73(5): 572-577.[42] Kamburoglu K,Yetimoglu NO,Altan H.Characterization of primary and permanent teeth using terahertz spectroscopy. Dentomaxillofac Radiol.2014;43(6):20130404.[43] 梁韵,陈柯.Er,Cr:YSGG激光对乳牙硬组织粘接性能影响的研究进展[J].口腔疾病防治, 2017,25(3):196-199. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||